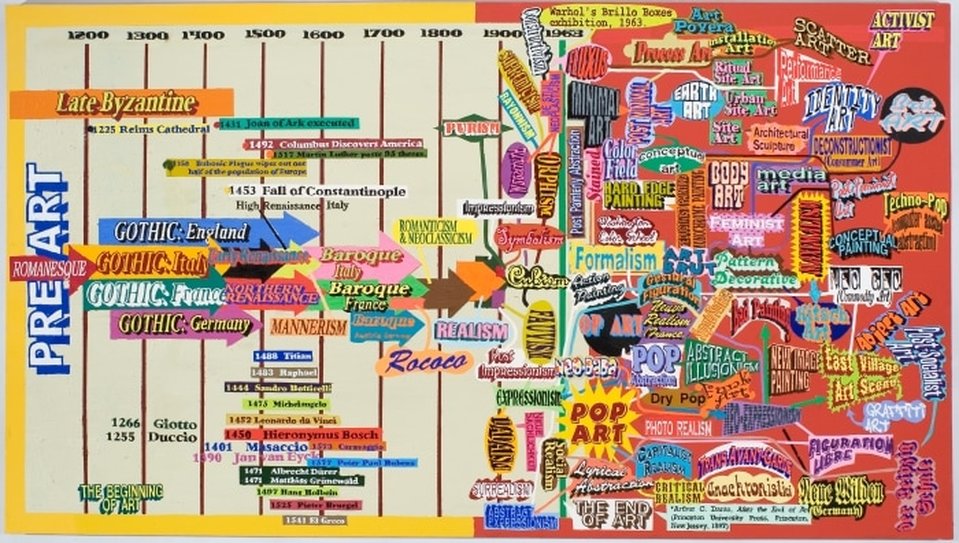
The history of art is immense, the earliest cave paintings pre-date writing by almost 27,000 years! If you’re interested in art history, the first thing you should do is take a look at these brief outlines of the artists, traits, works, and events that make up major art periods and how art evolved to present day.
Stone Age (30,000 b.c.–2500 b.c.)
Cave painting, fertility goddesses, megalithic structures
Lascaux Cave Painting, Woman of Willendorf, Stonehenge
Ice Age ends (10,000 b.c.–8,000 b.c.); New Stone Age and first permanent settlements (8000 b.c.–2500 b.c.)
Mesopotamian (3500 b.c.–539 b.c.)
Warrior art and narration in stone reliefStandard of Ur, Gate of Ishtar, Stele of Hammurabi’s Code
Sumerians invent writing (3400 b.c.); Hammurabi writes his law code (1780 b.c.); Abraham founds monotheism
Egyptian (3100 b.c.–30 b.c.)
Art with an afterlife focus: pyramids and tomb paintingImhotep, Step Pyramid, Great Pyramids, Bust of Nefertiti
Narmer unites Upper/Lower Egypt (3100 b.c.); Rameses II battles the Hittites (1274 b.c.); Cleopatra dies (30 b.c.)
Greek and Hellenistic (850 b.c.–31 b.c.)
Greek idealism: balance, perfect proportions; architectural orders(Doric, Ionic, Corinthian)
Parthenon, Myron, Phidias, Polykleitos, PraxitelesAthens defeats Persia at Marathon (490 b.c.);
Peloponnesian Wars (431 b.c.–404 b.c.); Alexander the Great’s conquests (336 b.c.–323 b.c.)
Roman (500 b.c.– a.d. 476)
Roman realism: practical and down to earth; the arch
Augustus of Primaporta, Colosseum, Trajan’s Column,Pantheon
Julius Caesar assassinated (44 b.c.); Augustus proclaimed Emperor (27 b.c.); Diocletian splits Empire (a.d. 292);
Rome falls (a.d. 476)
Indian, Chinese, and Japanese(653 b.c.–a.d. 1900)
Serene, meditative art, and Arts of the Floating World
Gu Kaizhi, Li Cheng, Guo Xi, Hokusai, Hiroshige
Birth of Buddha (563 b.c.); Silk Road opens (1st century b.c.); Buddhism spreads to China (1st–2nd centuries a.d.)
and Japan (5th century a.d.)
Byzantine and Islamic (a.d. 476–a.d.1453)
Heavenly Byzantine mosaics; Islamic architecture and amazing maze-like design
Hagia Sophia, Andrei Rublev, Mosque of Córdoba, the AlhambraJustinian partly restores Western Roman Empire (a.d. 533–a.d. 562); Iconoclasm Controversy (a.d. 726–a.d. 843); Birth of Islam (a.d. 610) and Muslim Conquests (a.d. 632–a.d. 732)
Middle Ages (500–1400)
Celtic art, Carolingian Renaissance, Romanesque, Gothic
St. Sernin, Durham Cathedral, Notre Dame, Chartres, Cimabue,Duccio, Giotto
Viking Raids (793–1066); Battle of Hastings (1066); Crusades I–IV (1095–1204); Black Death (1347–1351); Hundred Years’ War (1337–1453)
Early and High Renaissance (1400–1550)Rebirth of classical cultureGhiberti’s Doors, Brunelleschi, Donatello, Botticelli,
Leonardo, Michelangelo, RaphaelGutenberg invents movable type (1447); Turks conquer
Constantinople (1453); Columbus lands in New World (1492); Martin
Luther starts Reformation (1517)
Venetian and Northern Renaissance (1430–1550)The Renaissance spreads north- ward to France, the Low
Countries, Poland, Germany, and EnglandBellini, Giorgione, Titian, Dürer, Bruegel, Bosch, Jan van
Eyck, Rogier van der WeydenCouncil of Trent and Counter-Reformation (1545–1563);
Copernicus proves the Earth revolves around the Sun (1543
Mannerism (1527–1580)Art that breaks the rules; artifice over natureTintoretto, El Greco, Pontormo, Bronzino, CelliniMagellan circumnavigates the globe (1520–1522)
Baroque (1600–1750)Splendor and flourish for God; art as a weapon in the religious
warsReubens, Rembrandt, Caravaggio, Palace of VersaillesThirty Years’ War between Catholics and Protestants
(1618–1648)
Neoclassical (1750–1850)Art that recaptures Greco-Roman grace and grandeurDavid, Ingres, Greuze, CanovaEnlightenment (18th century); Industrial Revolution
(1760–1850)
Romanticism (1780–1850)The triumph of imagination and individualityCaspar Friedrich, Gericault, Delacroix, Turner, Benjamin
WestAmerican Revolution (1775–1783); French Revolution
(1789–1799); Napoleon crowned emperor of France (1803)
Realism (1848–1900)Celebrating working class and peasants; en plein air
rustic paintingCorot, Courbet, Daumier, MilletEuropean democratic revolutions of 1848
Impressionism (1865–1885)Capturing fleeting effects of natural lightMonet, Manet, Renoir, Pissarro, Cassatt, Morisot, DegasFranco-Prussian War (1870–1871); Unification of Germany
(1871)
Post-Impressionism (1885–1910)A soft revolt against ImpressionismVan Gogh, Gauguin, Cézanne, SeuratBelle Époque (late-19th-century Golden Age); Japan
defeats Russia (1905)
Fauvism and Expressionism (1900–1935)Harsh colors and flat surfaces (Fauvism); emotion distorting
formMatisse, Kirchner, Kandinsky, MarcBoxer Rebellion in China (1900); World War
(1914–1918)
Cubism, Futurism, Supremativism, Constructivism, De Stijl
(1905–1920)Pre– and Post–World War 1 art experiments: new
forms to express modern lifePicasso, Braque, Leger, Boccioni, Severini, MalevichRussian Revolution (1917); American women franchised
(1920)
Dada and Surrealism (1917–1950)Ridiculous art; painting dreams and exploring the
unconsciousDuchamp, Dalí, Ernst, Magritte, de Chirico, Kahlo
Disillusionment after World War I; The Great Depression
(1929–1938); World War II (1939–1945) and Nazi horrors;
atomic bombs dropped on Japan (1945)
Abstract Expressionism (1940s–1950s) and Pop Art
(1960s)Post–World War II: pure abstraction and expression
without form; popular art absorbs consumerismGorky, Pollock, de Kooning, Rothko, Warhol, LichtensteinCold War and Vietnam War (U.S. enters 1965); U.S.S.R.
suppresses Hungarian revolt (1956) Czechoslovakian revolt
(1968)
Postmodernism and Deconstructivism (1970– )Art without a center and reworking and mixing past stylesGerhard Richter, Cindy Sherman, Anselm Kiefer, Frank Gehry,
Zaha HadidNuclear freeze movement; Cold War fizzles; Communism collapses
in Eastern Europe and U.S.S.R. (1989–1991)
Source: http://www.dummies.com/education/art-appreciation/art-history-timeline/
Cave painting, fertility goddesses, megalithic structures
Lascaux Cave Painting, Woman of Willendorf, Stonehenge
Ice Age ends (10,000 b.c.–8,000 b.c.); New Stone Age and first permanent settlements (8000 b.c.–2500 b.c.)
Mesopotamian (3500 b.c.–539 b.c.)
Warrior art and narration in stone reliefStandard of Ur, Gate of Ishtar, Stele of Hammurabi’s Code
Sumerians invent writing (3400 b.c.); Hammurabi writes his law code (1780 b.c.); Abraham founds monotheism
Egyptian (3100 b.c.–30 b.c.)
Art with an afterlife focus: pyramids and tomb paintingImhotep, Step Pyramid, Great Pyramids, Bust of Nefertiti
Narmer unites Upper/Lower Egypt (3100 b.c.); Rameses II battles the Hittites (1274 b.c.); Cleopatra dies (30 b.c.)
Greek and Hellenistic (850 b.c.–31 b.c.)
Greek idealism: balance, perfect proportions; architectural orders(Doric, Ionic, Corinthian)
Parthenon, Myron, Phidias, Polykleitos, PraxitelesAthens defeats Persia at Marathon (490 b.c.);
Peloponnesian Wars (431 b.c.–404 b.c.); Alexander the Great’s conquests (336 b.c.–323 b.c.)
Roman (500 b.c.– a.d. 476)
Roman realism: practical and down to earth; the arch
Augustus of Primaporta, Colosseum, Trajan’s Column,Pantheon
Julius Caesar assassinated (44 b.c.); Augustus proclaimed Emperor (27 b.c.); Diocletian splits Empire (a.d. 292);
Rome falls (a.d. 476)
Indian, Chinese, and Japanese(653 b.c.–a.d. 1900)
Serene, meditative art, and Arts of the Floating World
Gu Kaizhi, Li Cheng, Guo Xi, Hokusai, Hiroshige
Birth of Buddha (563 b.c.); Silk Road opens (1st century b.c.); Buddhism spreads to China (1st–2nd centuries a.d.)
and Japan (5th century a.d.)
Byzantine and Islamic (a.d. 476–a.d.1453)
Heavenly Byzantine mosaics; Islamic architecture and amazing maze-like design
Hagia Sophia, Andrei Rublev, Mosque of Córdoba, the AlhambraJustinian partly restores Western Roman Empire (a.d. 533–a.d. 562); Iconoclasm Controversy (a.d. 726–a.d. 843); Birth of Islam (a.d. 610) and Muslim Conquests (a.d. 632–a.d. 732)
Middle Ages (500–1400)
Celtic art, Carolingian Renaissance, Romanesque, Gothic
St. Sernin, Durham Cathedral, Notre Dame, Chartres, Cimabue,Duccio, Giotto
Viking Raids (793–1066); Battle of Hastings (1066); Crusades I–IV (1095–1204); Black Death (1347–1351); Hundred Years’ War (1337–1453)
Early and High Renaissance (1400–1550)Rebirth of classical cultureGhiberti’s Doors, Brunelleschi, Donatello, Botticelli,
Leonardo, Michelangelo, RaphaelGutenberg invents movable type (1447); Turks conquer
Constantinople (1453); Columbus lands in New World (1492); Martin
Luther starts Reformation (1517)
Venetian and Northern Renaissance (1430–1550)The Renaissance spreads north- ward to France, the Low
Countries, Poland, Germany, and EnglandBellini, Giorgione, Titian, Dürer, Bruegel, Bosch, Jan van
Eyck, Rogier van der WeydenCouncil of Trent and Counter-Reformation (1545–1563);
Copernicus proves the Earth revolves around the Sun (1543
Mannerism (1527–1580)Art that breaks the rules; artifice over natureTintoretto, El Greco, Pontormo, Bronzino, CelliniMagellan circumnavigates the globe (1520–1522)
Baroque (1600–1750)Splendor and flourish for God; art as a weapon in the religious
warsReubens, Rembrandt, Caravaggio, Palace of VersaillesThirty Years’ War between Catholics and Protestants
(1618–1648)
Neoclassical (1750–1850)Art that recaptures Greco-Roman grace and grandeurDavid, Ingres, Greuze, CanovaEnlightenment (18th century); Industrial Revolution
(1760–1850)
Romanticism (1780–1850)The triumph of imagination and individualityCaspar Friedrich, Gericault, Delacroix, Turner, Benjamin
WestAmerican Revolution (1775–1783); French Revolution
(1789–1799); Napoleon crowned emperor of France (1803)
Realism (1848–1900)Celebrating working class and peasants; en plein air
rustic paintingCorot, Courbet, Daumier, MilletEuropean democratic revolutions of 1848
Impressionism (1865–1885)Capturing fleeting effects of natural lightMonet, Manet, Renoir, Pissarro, Cassatt, Morisot, DegasFranco-Prussian War (1870–1871); Unification of Germany
(1871)
Post-Impressionism (1885–1910)A soft revolt against ImpressionismVan Gogh, Gauguin, Cézanne, SeuratBelle Époque (late-19th-century Golden Age); Japan
defeats Russia (1905)
Fauvism and Expressionism (1900–1935)Harsh colors and flat surfaces (Fauvism); emotion distorting
formMatisse, Kirchner, Kandinsky, MarcBoxer Rebellion in China (1900); World War
(1914–1918)
Cubism, Futurism, Supremativism, Constructivism, De Stijl
(1905–1920)Pre– and Post–World War 1 art experiments: new
forms to express modern lifePicasso, Braque, Leger, Boccioni, Severini, MalevichRussian Revolution (1917); American women franchised
(1920)
Dada and Surrealism (1917–1950)Ridiculous art; painting dreams and exploring the
unconsciousDuchamp, Dalí, Ernst, Magritte, de Chirico, Kahlo
Disillusionment after World War I; The Great Depression
(1929–1938); World War II (1939–1945) and Nazi horrors;
atomic bombs dropped on Japan (1945)
Abstract Expressionism (1940s–1950s) and Pop Art
(1960s)Post–World War II: pure abstraction and expression
without form; popular art absorbs consumerismGorky, Pollock, de Kooning, Rothko, Warhol, LichtensteinCold War and Vietnam War (U.S. enters 1965); U.S.S.R.
suppresses Hungarian revolt (1956) Czechoslovakian revolt
(1968)
Postmodernism and Deconstructivism (1970– )Art without a center and reworking and mixing past stylesGerhard Richter, Cindy Sherman, Anselm Kiefer, Frank Gehry,
Zaha HadidNuclear freeze movement; Cold War fizzles; Communism collapses
in Eastern Europe and U.S.S.R. (1989–1991)
Source: http://www.dummies.com/education/art-appreciation/art-history-timeline/